Refraction of Light
Refraction of Light: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Lens, Centres of Curvature of a Lens, Angle of Refraction & Angle of Emergence etc.
Important Questions on Refraction of Light
An object of height is placed at from a concave lens of focal length . Select the correct size of the image.
An object is placed at a distance from a convex lens of focal length . Select the correct image distance and nature of the image.
The convex lens always gives small virtual image.
The power of lens depends on the focal length of the lens.
Velocity of light is greater in denser medium than in rarer medium.
What happens when the lens is thick?
The thickness of centre part of a thick lens is negligible.
The thickness of centre part of a thick lens is not negligible.
What does thick lens in optics means?
Assertion: Virtual images are always erect.
Reason: Virtual images are formed by diverging lenses only.
What is centre of curvature of a lens?
The ray coming out of a glass after refraction is known as the emergent ray.
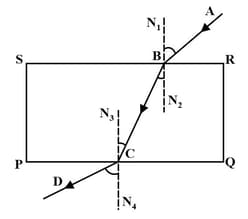
In an experiment to trace the path of ray through a glass slab, Shiva traced as shown in the figure. Out of AB, BC and CD, _____ is the emergent ray.
A small object is placed in front of convex lens of focal length , such that a virtual image is formed at a distance of . The magnification produced is
A _____ (convex / concave) lens can produce both real and virtual images.
Which lens diverges the light rays falling on it?
Which lens is used as a magnifying glass - convex lens or concave lens?
An object is placed at a distance of from the convex lens of focal length . If object height is then find the position and nature of the image.
When light fall obliquely on the surface of a thick glass slab, a part of the light reflects at the surface and a part of it refracts.
Light falls obliquely on the surface of a thick glass slab as shown in the figure. Which statement among the following is correct?